Android的定位技术 在开发Android位置相关的应用的时候,可以从GPS或者网络获取用户位置,通过GPS能够获得最精确的信息,但是仅适于户外,不但耗电,而且不能及时返回用户需要的信息,使用网络能从发射塔和Wifi信号获得用户位置,提供一种适用于户内和户外的获取位置信息的方式。不但相应速度迅速,而且更加省电。
在Android系统中,开发人员需要使用如下的类来访问定位服务。
LocationManager:该类提供系统定位服务访问功能
LocationListener :当位置发生变化的时候,该接口从LocationManager中获得通知
Location:该类表示特定时间地理位置变化信息,位置由经度,纬度,UTC时间戳以及可选的高度,速度,方向等组成
获取可用定位服务
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState ) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState ) ; setContentView(R.layout .activity_main ) ; tv= (TextView) findViewById(R.id .tv ) ; LocationManager manager = (LocationManager) getSystemService(LOCATION_SERVICE) ; List<String> list = manager.getAllProviders() ; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder() ; for (String locationResouse:list ){ sb.append(locationResouse+"\n" ); } tv.setText(sb .toString () ); }
查看位置源属性
LocationManager manager = (LocationManager) getSystemService(LOCATION_SERVICE); LocationProvider provider = manager.getProvider(LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER); int accuracy = provider.getAccuracy();StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append ("GPS Info:\n" ); switch (accuracy) { case Criteria.ACCURACY_HIGH: sb.append ("accuracy:High\n" );break ; case Criteria.ACCURACY_LOW: sb.append ("accuracy:Low\n" );break ; case Criteria.ACCURACY_MEDIUM: sb.append ("accuracy:Medium\n" );break ; default :break ; } int power = provider.getPowerRequirement();switch (power ) { case Criteria.POWER_LOW: sb.append ("power:Low\n" );break ; case Criteria.POWER_HIGH: sb.append ("power:High\n" );break ; case Criteria.POWER_MEDIUM: sb.append ("power:Medium\n" );break ; default :break ; }
监听位置变化事件
requestLocationUpdates(provider , minTime , minDistance , listener )
参数说明如下:
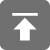
provider: 注册的provider的名称minTime: 通知间隔的最小事件,单位是毫秒,系统为了省电可以延长该时间minDistance:更新通知的最小变化距离,单位是米。 listener: 用于处理通知的监听器,可以是下表的其中一种:
Android 网络访问技术 使用HttpURLConnection访问网络 HttpURLConnection 位于java.net包中,用于发送Http请求和获取Http响应,由于该类是抽象类,不能直接实例化对象,需要使用URL的openConnection()方法来获取.
创建HttpURLConnection对象:
uri = new URL("http://php.weather.sina.com.cn/xml.php&city=" + URLEncoder.encode (“惠州”, "gb2312" ) + "&password=DJOYnieT8234jlsK&day=0" );
HttpURLConnection urlConnection = (HttpURLConnection)url.open Connection() ;
uri = new URL(“http: HttpURLConnection urlConnection = (HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection(); urlConn.setDoInput(true ); urlConn.setDoOutput(true ); urlConn.setRequestMethod("POST" ); urlConn.setUseCaches(false ); urlConn.setInstanceFollowRedirects(false ); urlConn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type" ,"application/x-www-form-urlencoded" ); urlConn.connect(); out = new DataOutputStream(urlConn.getOutputStream());String content =“city="+ URLEncoder.encode(“惠州”, " gb2312")+ " &password=DJOYnieT8234jlsK&day=0 "); out.writeBytes(content); // 写入输出流 out.flash(); out.close();
int responseCode = conn.getResponseCode() if (responseCode = = HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) { }
InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(urlConn.getInputStream()); BufferedReader buffer = new BufferedReader(in); Stream inputLine = null ; While ((inputLine=buffer .readLine())!=null ){ result += inputLine+”\n”; }
In.close() urlConn.disconnect()
<uses-permission android:name ="android.permission.INTERNET" />
访问网络需要在工作线程中完成否则会产生ANR
使用HttpClient访问网络 一般情况下如果只需完成简单的页面提交请求并获取服务器的响应,可以使用HttpURLConnection来实现,而对于比较复杂的联网操作则需要使用Apache组织提供的一个HttpClient来访问网络。
Get方式:
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet("http://php.weather.sina.com.cn/xml.php&city=" + URLEncoder.encode (“惠州”, "gb2312" ) + "&password=DJOYnieT8234jlsK&day=0" );
HttpClient httpclient = new DefaultHttpClient()
调用HttpClient对象的excute()方法发送请求,返回一个HttpResponse对象。
HttpResponse httpresponse= httpclient.execute(httpget)
If(httpresponse .getStatusLine () .getStatusCode() ==HttpStatus.SC_OK){}
调用HttpResponse的getEntity()方法,可以获得包含服务器响应内容的HttpEntity对象,通过该对象可以获取服务器的响应内容。
EntityUtils .to String(httpresponse .getEntity () );EntityUtils. toByteArray (httpresponse.getEntity() ); httpresponse.getEntity() .getContent()
Post方式:
HttpPost httppost = new HttpPost(“http :/ / php .weather .sina .com .cn / xml .php ”) ;
如果需要发送请求参数,可调用HttpGet、HttpPost共同的setParams(HttpParams params)方法来添加请求参数;也可调用HttpPost对象的setEntity(HttpEntity entity)方法来设置请求参数。
List<NameValuePair> param = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>() ; Param .new BasicNameValuePair(“city ”,”huizhou ”) );Param .new BasicNameValuePair(“password ”, “DJOYnieT8234jlsK”) );Param .new BasicNameValuePair(“day ”, “0”) );Httppost .Entity(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(param ,”utf -8”) );
HttpClient httpclient = new DefaultHttpClient()
调用HttpClient的execute方法发送请求返回一个HttpResponse对象
HttpResponse httpresponse= httpclient.execute(httppost)
If(httpresponse .getStatusLine () .getStatusCode() ==HttpStatus.SC_OK){}
调用HttpResponse的getEntity方法通过该方法获得HttpEntity对象,通过该对象获取服务器的响应信息。
Http请求乱码问题解决方案 使用EntityUtils的toString方法,传递编码,默认编码是ISO-8859-1
charset = getContentCharSet(entity ) ; result = EntityUtils .to String(entity , charset ) ; public static String getContentCharSet(final HttpEntity entity ) { String charset = null; if (entity.getContentType() != null) { HeaderElement values[] = entity.getContentType() .getElements() ; if (values.length > 0 ) { NameValuePair param = values[0 ] .getParameterByName("charset" ) ; if (param != null) { charset = param.getValue() ; } } } if (StringUtils .Empty(charset ) ){ charset = "UTF-8" ; } return charset; }